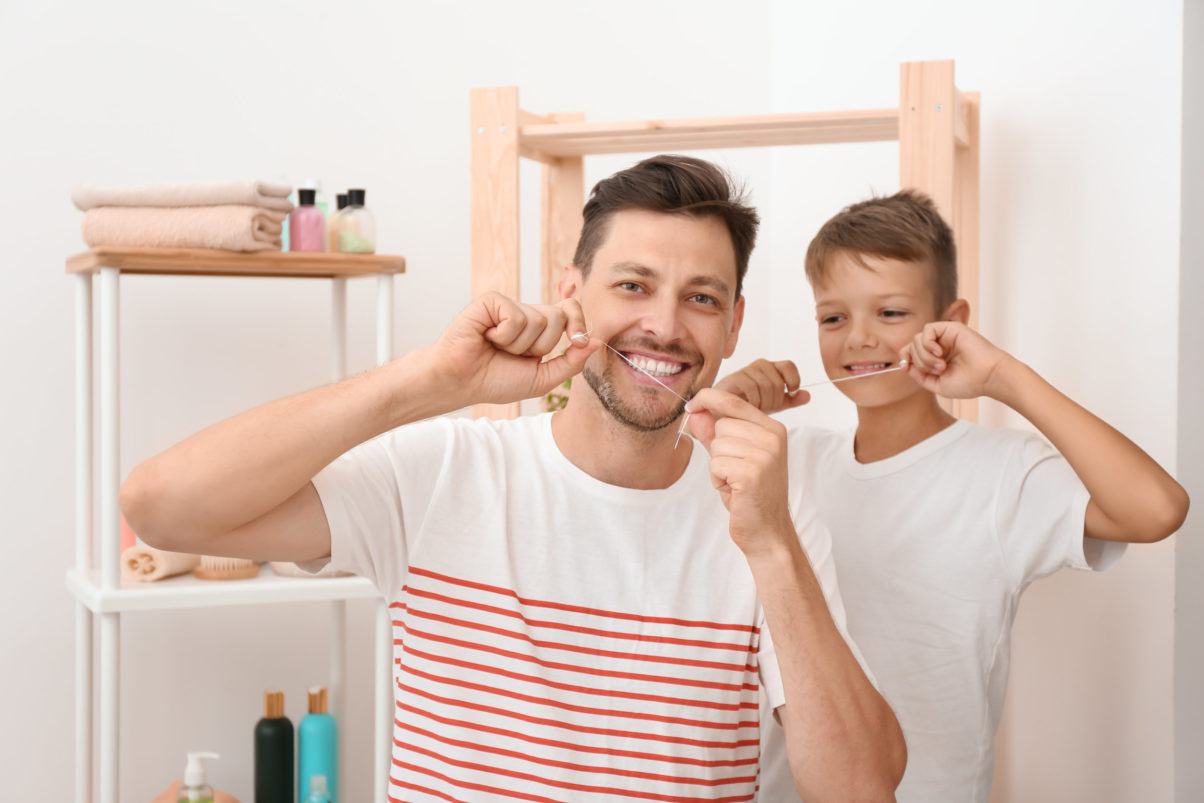
If you have trouble committing to a daily flossing routine, you aren’t alone. According to surveys, nearly one-third of Americans don’t floss regularly. Unfortunately, this puts them at a higher risk for tooth decay and periodontal disease. Here’s what happens when you don’t incorporate flossing as part of your daily oral hygiene regimen.
Do You Really Need to Floss?
Interdental cleaning or “flossing” helps remove debris and dental plaque from between teeth. By helping to clean these hard-to-reach tooth surfaces, floss helps reduce the likelihood of periodontal disease and tooth decay, while also reducing bacteria responsible for bad breath.
According to the American Dental Association, regular flossing is an important part of healthy oral hygiene. Just going a couple of days without flossing will allow plaque to build up. Over time, this plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dentist.
While brushing and mouthwash are critical for removing food particles and plaque; they are only doing part of the job. The bacteria that cause gum infections and cavities build up in the areas between teeth and inside the pockets under the gums. The only effective way to get them out is by flossing and getting regular professional cleanings at the dentist. If you don’t floss, you are at a higher risk of developing cavities between the teeth. You are also at an increased risk for gum disease, which can lead to all sorts of other serious issues.
Complications of Gum Disease
When you allow bacteria to build up between your teeth and in the pockets beneath your gums, inflammation can develop. Known as periodontitis, this inflammation can damage the soft tissue in your mouth and destroy the bone that supports your teeth. As gum disease progresses, you can develop all sorts of troubling complications, including tooth and bone loss.
According to the Mayo Clinic, some research also suggests the bacteria that cause periodontitis can migrate into your bloodstream through oral tissue and affect your lungs, heart and other critical parts of your body. For instance, studies indicate that periodontitis could be linked with rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory disease, stroke and coronary artery disease.
Avoiding Potential Problems
While more research is needed to determine just how much gum disease affects our overall health; experts are certain it can result in tooth and bone loss. You can reduce your risk by brushing twice a day and flossing at least once, based on these guidelines from the ADA. You should also schedule regular checkups and cleanings with your local dentist. In addition to removing tartar buildup, your dentist can look for potential signs of tooth decay and gum disease and recommend treatments to head off minor issues before they evolve into painful problems.


 Previous Article
Previous Article